Veganism transcends the realm of personal dietary choice and lifestyle, carrying profound political implications that challenge established norms, institutions, and power structures. At its core, veganism represents a radical departure from the status quo, advocating for a fundamental shift in our relationship with animals, the environment, and the global food system.
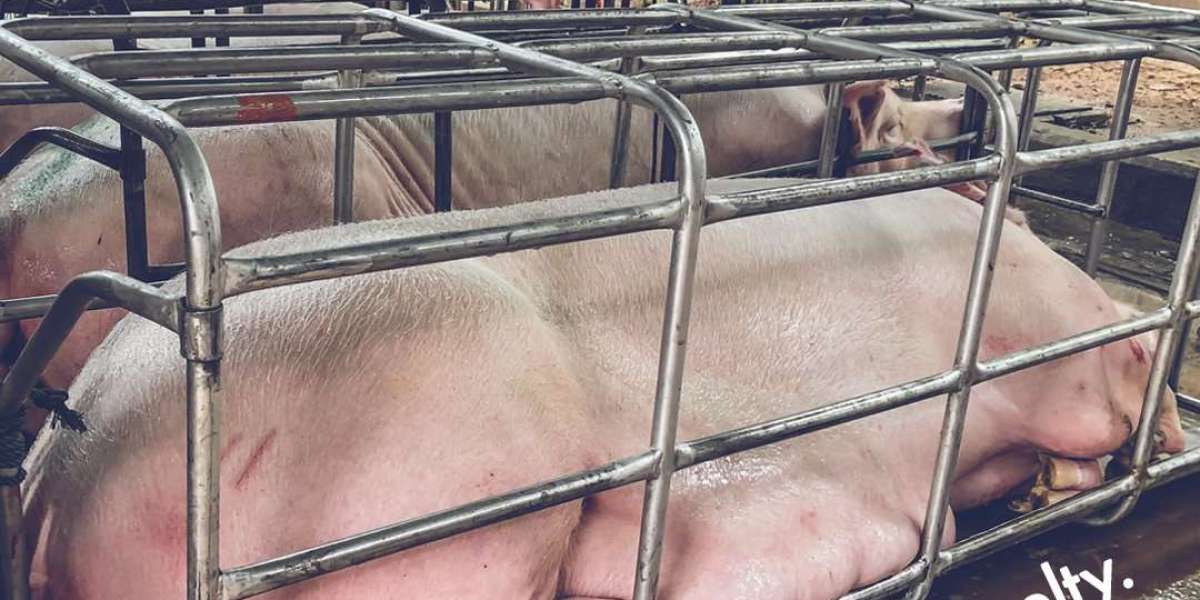
One of the key political implications of veganism lies in its challenge to entrenched systems of oppression and exploitation. By rejecting the commodification and exploitation of animals for human purposes, veganism confronts the inherent injustice and inequality perpetuated by industrialized animal agriculture. It calls into question the ethics of treating sentient beings as mere commodities, and advocates for a more equitable and compassionate society where the rights and welfare of all living beings are respected and protected.
Furthermore, veganism carries significant environmental and social justice implications, particularly in the context of climate change and global food security. The intensive production of animal products contributes to deforestation, habitat destruction, and biodiversity loss, exacerbating environmental degradation and threatening the livelihoods of communities around the world. By promoting plant-based diets and sustainable food systems, veganism offers a pathway towards mitigating the impacts of climate change, conserving natural resources, and addressing food insecurity on a global scale.
Moreover, veganism intersects with broader political movements and ideologies, including animal rights, environmentalism, feminism, and anti-capitalism. Veganism challenges the anthropocentric worldview that privileges human interests over those of other species, and calls for a more holistic and inclusive approach to ethics, justice, and sustainability. It aligns with movements for social justice and liberation, recognizing the interconnectedness of oppressions and advocating for a more just and equitable world for all beings.
In addition, veganism carries implications for public policy and governance, influencing debates and decisions around issues such as food and agricultural subsidies, animal welfare regulations, and public health initiatives. As veganism continues to gain momentum as a social and political movement, policymakers are increasingly called upon to address the systemic challenges and injustices perpetuated by the industrialized food system, and to promote policies that support a transition towards more sustainable, ethical, and plant-based diets.
In conclusion, the political implications of veganism are far-reaching and transformative, challenging entrenched power structures, advocating for social and environmental justice, and promoting a more compassionate and sustainable vision for the future. As individuals and communities continue to embrace veganism as a political stance and lifestyle choice, we have the opportunity to create positive change and build a more just and equitable world for all beings.